The Basics
The prostate is a small gland in men that’s usually about as big as a walnut, but it can be bigger in order men. The prostate makes seminal fluid (the liquid part of semen that carries sperm).
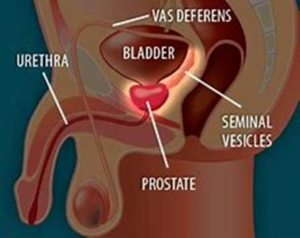
Prostate cancer begins in the cells of your prostate. Normally new cell grow and divide as your body needs them, then die when they’re old and damaged, but if you have cancer, new cells form when your body doesn’t need them or damaged cells don’t need them or damaged cell don’t die when they should. The extra cells build up and from a mass of tissue called a growth or tumor . Unlike other cancers, prostate censer normally grows very slowly.
Testing
In order to diagnose and stage your canser, your doctor will likely start with a digital rectal exam(DRE), where he feels your prostate for tumors by plcing a finger in your rectum. You’ll also need at least some of the following :
Prostate-Specific Antigen (PSA) test – PSA is a protein made in your prostate. Your doctor will take a blood sample to measure it. A higher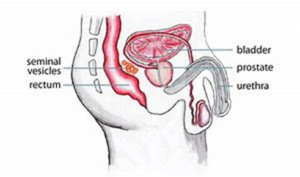 number means you’re more likely to have cancer, or that it has spread. if you’re more likely to have cancer, or that it has spread. If you’re already being treated, your PSA can help your doctor Know if your treatment is working.
number means you’re more likely to have cancer, or that it has spread. if you’re more likely to have cancer, or that it has spread. If you’re already being treated, your PSA can help your doctor Know if your treatment is working.
Biopsy– your doctor will remove A sample of tissue to study under a microscope.
Transrectal ultrasound (TRUS)- your doctor will insert a small probe in to your rectum. The probe uses sound waves to create an image of your prostate. Your doctor may also use a TRUS during a biopsy.
Staging
If tests show that you have cancer, your doctor will look at the stage to decide the most effective treatment. In addition to your PSA levels, your doctor will also look at your Gleason Score and use the TNM system to grade and stage your cancer.
The Gleason system looks at your cancer’s grade – how much or little cancer cells look like healthy cells. A Lower score means your cancer is less likely to be aggressive and spread. Your Gleason score will likely range from 6 to 10.
The TNM system is another tool doctor’s use in staging. It answers the following questions:
Tumor (T): what is the tumor?
Node (N): has the tumor spread to any lymph nodes?
Metastasis (M): has the cancer spread to other parts of the body?
Prostate cancer stages
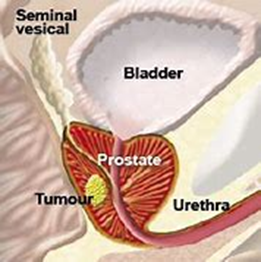
Stage 1: Your censer cell look very much like healthy cells and haven’t spread out of the prostate. Tumors can’t be felt during an exam or seen with imaging tests.
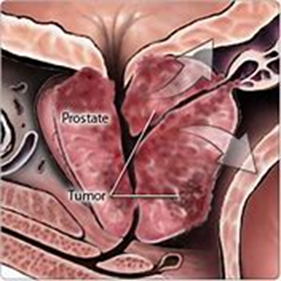
Stage 2: Your cancer is still only in the prostate, but the cells might be the cells might b aggressive and don’t look like normal cells. Your doctor might be able to feel tumors during an exam.
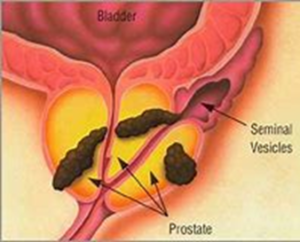
Stage 3: your cancer has spread outside the prostate to nearby tissue like the seminal vesicles.

Stage 4: your cancer has spread to other parts of your body like your bones, liver or lungs. This is called metastasis.
Your doctor will help you decide which treatment option is right for you. in general, your treatment will depend on your:
- Age
- General Health
- Cancer Stage
- Cancer grade
- Symptoms
- Possible side effects
Treatment options include:
Active Surveillance –This may be an option if you have early-Stage or older or have other health concerns. This means you don’t immediately treat your cancer. Instead, you have regular checkups for testing.
Watchful waiting is similar, but may involve less-intense testing and follow-up.
Radiation – This is an option for all Stages of prostate cancer. Radiation therapy uses high-energy rays to kill cancer cells. Radiation is sometimes used along with surgery, or as a way to help ease pain if you have late-stage cancer .Radiation treatments usually last only a few minutes and are given five days a week for several weeks.
Surgery- This is usually an option if your cancer hasn’t spread outside your prostate. If you have a prostatectomy, all or part of your prostate is removed. During a well as the seminal vesicle and some surrounding tissue is removed.
Hormone Therapy (or androgen deprivation therapy-ADT) –This is often an option with Advanced Prostate cancer, but can be used in other states as well. Male hormones like testosterone cause prostate cancer to grow. To prevent this, hormone levels, or stops them form interacting with prostate cancer’s growth.
Hormone therapy can be given as a pill, implant or injection. it can also include surgery where a doctor removes your testicles.
Cryotherapy– this is normal used for early –stage prostate cancer,or if your cancer returns after radiation therapy.it uses very cold gases to freeze and destroy prostate tissue. Cryotherapy is less invasive than surgery.
Chemotherapy– This is normally used for Advanced prostate cancer.it uses one or a combination of medicines to kill cancer cells or stop them from dividing.but it can also harm your body,s healthy cells.if you have prostate cancer, you will generally get chemotherapy in pills or as injections in to your vein.you usually take chemo in cycles of a few weeks with a break in between, so your body ca recover.
Immunotherapy– Also called vaccine therapy, this is used if you have advaved cancer. It uses a vaccine to boost your immune system so it can kill the cancer cells in your body.
The vaccine wses your own white Blood cells.these are combined with a protein from peostate cancer cells, then injected back in to your body to help your immune system attack the cancer.this is usually done three times a month.
Other treatments, like high intensity focused ultrasound (HIFU), may be an option. This uses sound waves to kill cancer cells. HIFU isn,t widely-used yet, so ask your doctor for more information.
Along with treatments that kill cancer cells, your plan also may aim to relueve symptoms or treat complications caused by cancer. This is called palliative care. Talk to your doctor to learn more.
Cancer in your bones
If cancer spreads outside your prostate, it often goes to your bones first. This can be very painful and lead to problems like fractures. But there are options that specifically treat bone metastases.
These medicines help to relieve pain, slow your cancer,s growth or prevent bone fractures. Some can even help prevent cancer spreading to your bones in their first place.

